Leave Your Message
In today's rapidly evolving industry, the role of Technical Ceramic is becoming increasingly crucial. Experts like Dr. Sarah Thompson, a leading figure in materials science, emphasize, "Technical Ceramics are key to enhancing performance in various applications." This insight underscores the material's significance in sectors such as aerospace, electronics, and automotive.
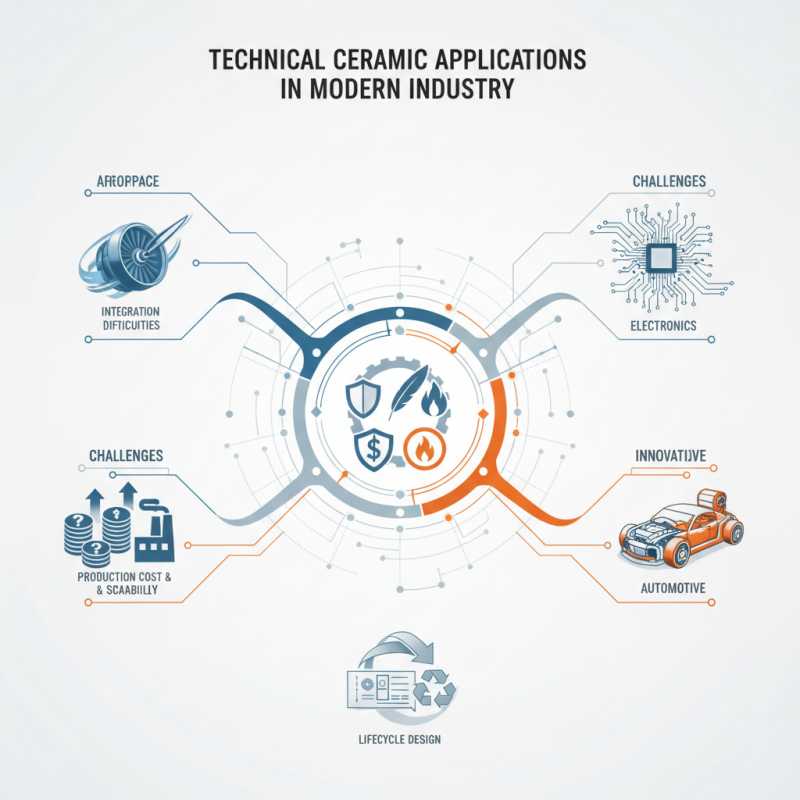
Technical Ceramics provide unique properties. They are strong, lightweight, and resistant to high temperatures. For instance, in aerospace, they are used in turbine engines to improve efficiency and reduce weight. However, not all applications have been fully explored. Industries still face challenges in integrating Technical Ceramics seamlessly into existing processes.
Moreover, there is room for innovation. Manufacturers often struggle with production costs and scalability. Thus, engineers must rethink designs and consider the lifecycle of these materials. This evolving landscape demands continuous improvement and adaptation. Understanding both the benefits and the challenges of Technical Ceramics is essential for future advancements.
Technical ceramics play a crucial role in modern industry, offering unique properties that enhance performance. These materials are known for their excellent hardness, high thermal stability, and remarkable wear resistance. Many industries rely on these characteristics to improve product durability and efficiency. For example, advanced ceramics are employed in aerospace components, such as turbine blades, where high temperatures and stress are common.
Not all technical ceramics are the same. Each type has specific attributes suited for different applications. For instance, alumina ceramics may excel in cutting tools, whereas zirconia ceramics shine in dental applications. However, the selection process can be challenging. Engineers must consider factors like cost, material strength, and desired outcomes. Sometimes, the best choice may not be obvious, and mistakes can lead to performance issues.
In addition, the manufacturing process of technical ceramics can be complex. Creating precise shapes often requires advanced techniques. The sintering process, for example, is critical for achieving desired densities and properties. Still, variations in this process can affect quality and consistency. Understanding these intricacies is vital for industry professionals, yet many encounters issues that prompt reflection and improvement in their approaches.
| Application | Ceramic Type | Key Properties | Industry |
|---|---|---|---|
| Insulation Components | Electrical Ceramics | High dielectric strength, thermal stability | Electronics |
| Cutting Tools | Cermets | High hardness, wear resistance | Manufacturing |
| Medical Implants | Bioceramics | Biocompatibility, corrosion resistance | Healthcare |
| Abrasive Grinding Wheels | Silicon Carbide | High thermal conductivity, hardness | Metalworking |
| Refractories | Alumina Ceramics | High melting point, thermal stability | Metallurgy |
| Sensor Protection | Piezoelectric Ceramics | Sensitivity, stability | Automotive |
Technical ceramics are increasingly finding applications across various industries due to their unique properties. The aerospace sector relies on these materials for components that demand high strength and thermal stability. Lightweight ceramic matrix composites are essential in aircraft designs, enhancing fuel efficiency and performance.
The medical field also makes significant use of technical ceramics. Bioceramics are employed in implants due to their biocompatibility and durability. These materials can withstand the harsh conditions of the human body, providing long-term solutions for patients.
Tips: When considering the use of technical ceramics, evaluate the specific requirements of your application. Not all ceramics perform equally in every situation. Experimentation is often needed to identify the right type.
In the automotive industry, technical ceramics play a role in engine components that require resistance to wear and heat. However, the cost of production can be high. It's essential to balance performance benefits with budget constraints.
Tips: Investigate alternative materials if costs exceed your budget. Sometimes, hybrids can provide a solution. Continuous innovation in this area means there are often unexpected options available.
Technical ceramics play a vital role in modern manufacturing. These materials are known for their exceptional hardness and resistance to heat. They are widely utilized in various industries, from aerospace to electronics.
In the aerospace sector, technical ceramics are used in components that endure extreme conditions. For example, ceramic matrix composites are critical for turbine blades. These materials can withstand high temperatures and pressures, ensuring safety and efficiency.
Tip: Consider exploring the properties of different ceramics. Not all ceramics are the same, and each type has unique benefits. Understanding their characteristics helps in selecting the right material.
Electronics also benefit from technical ceramics. Insulating ceramics are essential in electronic components to prevent current leakage. They are lightweight and can handle harsh environments, making them perfect for various applications.
Tip: When designing electronic devices, take note of ceramic insulators' thermal stability. This can enhance device performance but also has limits. Balancing efficiency and durability is key.
While technical ceramics offer many advantages, they can be brittle. Careful consideration is needed when designing products. Not every application will benefit from ceramics. Sometimes, metal or polymer might be a better option. It's essential to analyze all choices before finalizing a design.

The field of technical ceramics has seen remarkable innovations. New materials have been developed that enhance performance in various applications. These advancements include improved strength, durability, and thermal resistance. Technical ceramics are now essential in aerospace, medical, and automotive industries. They offer solutions that metals simply cannot match, especially in extreme environments.
One notable innovation is the creation of bioinert ceramics. These materials are used in medical implants, promoting better integration with human tissue. However, challenges remain in long-term stability and biocompatibility. The manufacturing processes also require refinement, as inconsistencies can affect the final product’s performance. While many companies strive for perfection, there are instances of defects that need attention.
Moreover, the development of transparent ceramics opens new doors in optics and electronics. Light transmission quality is impressive, yet manufacturing can be costly and complex. Industry professionals often reflect on these hurdles, understanding that while progress is occurring, there is still a long way to go. Balancing quality and cost remains a pivotal challenge in the pursuit of better technical ceramic applications.
The use of technical ceramics in industry is evolving rapidly. Advanced ceramics showcase unique properties like high strength and thermal stability. By 2025, the global market for technical ceramics is expected to reach approximately $130 billion. This rise indicates a significant demand in sectors like electronics and aerospace.
However, challenges persist. The high cost of raw materials can hinder accessibility. Moreover, the complexity of manufacturing processes creates hurdles for small businesses. Innovations in 3D printing are promising but still in early stages. There’s a gap between potential and reality.
Environmental concerns also affect the adoption of technical ceramics. The production processes may lead to waste and energy consumption issues. Studies indicate that improving sustainability in ceramics is essential. Without addressing these challenges, growth could stagnate. The industry must reflect on practices and seek solutions.