Leave Your Message
Choosing the right refractory sagger is vital for many industries. These tools protect fragile products during high-temperature processes. A bad choice can lead to costly mistakes.
When selecting a refractory sagger, consider your specific needs. Different materials and designs serve unique purposes. Think about the temperature ranges and the products you will be handling. Some saggers may not withstand intense conditions.
Reflect on your options carefully. Not every sagger is built the same. Misjudging can result in damage. Analyze your production requirements and budget constraints. The right refractory sagger can greatly enhance efficiency. Don't overlook the importance of expert advice.
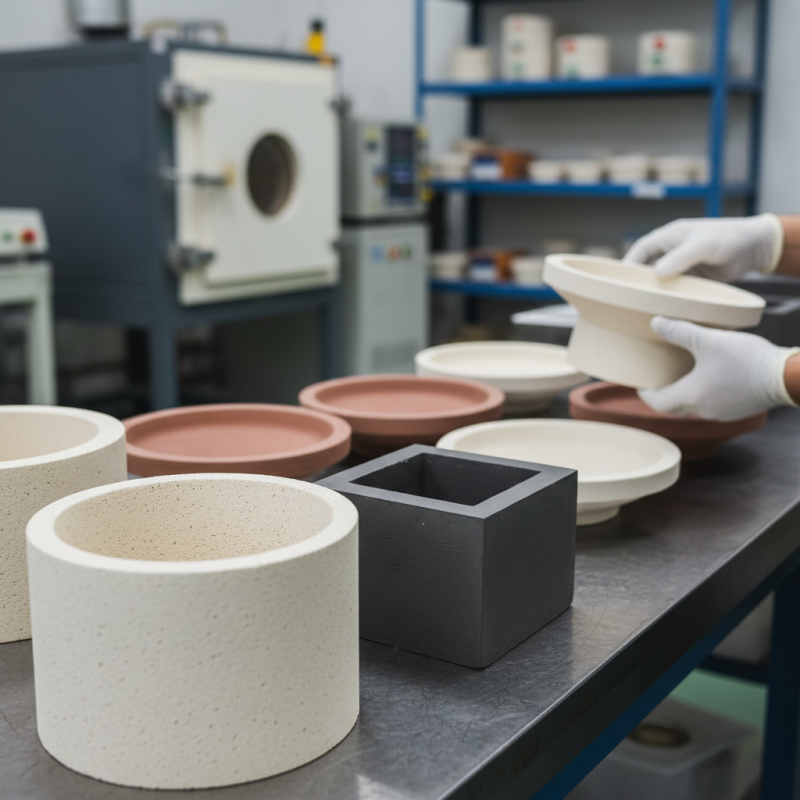

Refractory saggers play a crucial role in various industrial processes. Their primary function is to support and protect ceramic components during firing. High temperatures can cause materials to deform or break. Sagger design must account for these extreme conditions. Proper usage reduces the risk of damage and ensures consistent product quality.
According to industry reports, the global refractory market is projected to reach $35 billion by 2025. This surge is driven by increasing demand in sectors like construction and aerospace. Efficient saggers can enhance productivity by minimizing material waste. When choosing a sagger, consider factors such as thermal conductivity and chemical resistance. These properties influence how well a sagger will perform under stress.
Yet, it is essential to recognize that not all saggers are created equal. Some may not withstand repeated high-temperature cycles. Testing is key to determining durability. Additionally, consider costs versus benefits. A cheaper sagger might lead to frequent replacements, increasing overall expenses. Striking the right balance is vital for operational efficiency.
Choosing the right refractory sagger is essential for optimal performance in industrial applications. There are several key factors to consider when making your selection. First, the material composition of the sagger is important. Different materials can withstand varying temperatures and chemical environments. For example, some saggers provide better insulation, while others are more resilient against thermal shock.
Tip: Assess the specific temperatures your application will reach. This helps ensure that the refractory sagger meets the necessary heat resistance levels.
Another factor is the size and shape of the sagger. Ensure that the design fits well within your kiln or furnace setup. An ill-fitting sagger can lead to failure during operations. Pay attention to the weight of the sagger as well. A heavier sagger can be more stable but may be harder to handle.
Tip: Always measure your kiln dimensions accurately. It’s easy to overlook this detail but crucial for compatibility.
Lastly, examine the longevity and durability of the sagger. While a lower price may be tempting, consider the potential costs of replacing saggers frequently. Investigate user reviews or industry feedback to gauge performance over time. Take your time to reflect on these elements before making a choice.
When choosing refractories for saggers, consider the materials available. Common options include alumina, silica, and magnesia. Each material has distinct properties, impacting performance in high-temperature settings. Alumina is known for its strength and thermal stability. Silica offers good insulation but has a lower melting point. Magnesia is resilient under extreme conditions but can be expensive.
Evaluating these materials is crucial. For example, if you need high thermal shock resistance, alumina may be your best bet. However, remember that performance can vary depending on the manufacturing process. Sometimes, saggers fail due to improper material choices rather than design flaws. It’s essential to analyze your specific application.
In production, monitor how your chosen refractory interacts with the products. Some materials may cause contamination or affect final quality. Testing is vital before full-scale implementation. A small batch can reveal weaknesses. Reflect on the performance. Adjustments may be necessary. Finding the right refractory sagger involves ongoing evaluation and flexibility.
Choosing the right refractory sagger involves understanding your specific needs. The size and shape of saggers are crucial in ensuring effective firing results. It’s important to evaluate the dimensions of your kiln and the materials you intend to use. A sagger that is too small may not hold your products well, leading to defects.
When considering size, measure the dimensions of your products. Ensure the sagger can accommodate height and width comfortably. Additionally, consider the shape of your items. Some may require custom shapes to avoid deformation. Be aware that irregular shapes can complicate the choice of sagger.
**Tips:** Always allow extra space for thermal expansion. This helps prevent damage. Test different sizes with sample products. Observe how they react in the kiln. Adjust your choice based on these outcomes. Ignoring these details could result in costly errors. Pay close attention to both size and shape requirements for the best results.
| Size (cm) | Shape | Capacity (kg) | Material | Temperature Resistance (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 x 20 | Rectangular | 10 | Silica | 1250 |
| 40 x 30 | Square | 15 | Alumina | 1400 |
| 50 x 25 | Elliptical | 20 | Mullite | 1600 |
| 35 x 15 | Round | 8 | Fireclay | 1200 |
| 60 x 40 | Custom | 25 | High Alumina | 1700 |
Maintaining and using refractory saggers effectively can significantly affect your production process. A refractory sagger, crucial in high-temperature applications, provides support and protection to delicate ceramic materials. Industry reports suggest that improper handling can lead to early wear and increased costs. Regular inspections of your saggers are essential. Look for signs of wear or damage after each use.
Tips: Ensure your saggers are stored in a dry and stable environment. Humidity can cause unexpected changes in properties. Use soft tools for handling to avoid surface scratches or chips.
During operation, it's important to monitor the temperature closely. Sudden temperature fluctuations can stress the materials and lead to failure. A study found that over 30% of refractor saggers fail due to thermal shock. Routine cleaning can prolong their life. Dust and debris build-up can affect performance.
Tips: Use a gentle cleaning solution. Avoid abrasive materials that could damage your saggers. It's a small step but can save you money over time. Regularly update your maintenance procedures based on the latest industry guidelines to ensure you’re following best practices.






