Leave Your Message
Zirconia Ceramic has emerged as a groundbreaking material in various modern applications due to its remarkable properties and versatility. This comprehensive guide aims to unravel the myriad benefits of Zirconia Ceramic, showcasing why it has become a preferred choice across industries such as dentistry, aerospace, and manufacturing. With its exceptional strength, high fracture toughness, and resistance to wear and corrosion, Zirconia Ceramic not only enhances durability but also contributes to aesthetic appeal in products ranging from dental crowns to cutting tools. In this blog, we will explore the top reasons why Zirconia Ceramic stands out as a material of choice in contemporary innovations, highlighting its scientific advantages and practical applications that make it indispensable in today's technological landscape.

Zirconia ceramic has emerged as a revolutionary material in various modern applications due to its unique properties. One of its most notable advantages is its exceptional strength and durability. Unlike conventional ceramics, zirconia exhibits high resistance to fracture and wear, making it an ideal choice for dental implants, prosthetics, and cutting tools. This incredible toughness allows zirconia to withstand extreme conditions without compromising structural integrity, a vital factor in industries that demand reliability and performance.
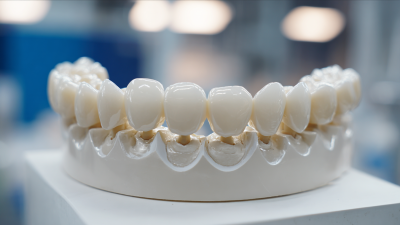
Another significant benefit of zirconia ceramic is its biocompatibility. This property is particularly crucial in medical applications, as zirconia is less likely to induce adverse reactions when in contact with biological tissues. Its smooth surface and ability to integrate seamlessly with bone further enhance its suitability for implants, leading to improved longevity and patient outcomes. Additionally, zirconia's resistance to corrosion and staining ensures that it maintains its aesthetic appeal, making it a popular choice for dental crowns and restorations, where both function and appearance are paramount.
Zirconia ceramic has emerged as a transformative material in both dental and medical fields, renowned for its exceptional strength, durability, and biocompatibility. In dentistry, zirconia is primarily used for crowns, bridges, and implants, providing a natural appearance that blends seamlessly with existing teeth. The material's resistance to wear and its ability to withstand significant chewing forces make it an ideal choice for restorative applications.
When considering zirconia ceramics for dental work, it’s essential to choose a reputable dental professional who is experienced in using this material. Tip: Always inquire about the quality of the zirconia used in your dental procedure to ensure optimal results and longevity. In the medical field, zirconia's biocompatibility allows for applications in surgical tools and implantable devices, minimizing the risk of rejection and infection.
Another important aspect is the aesthetic versatility of zirconia ceramics, which allows for a variety of shades and translucency levels. Tip: Discuss your aesthetic goals openly with your dentist to select the right shade and type of zirconia that meets your needs. This ensures that the final results not only meet functional requirements but also psychological and cosmetic expectations.
Zirconia ceramic is revolutionizing both the aerospace and automotive industries with its superior properties, making it a game changer in these high-demand sectors. According to a report by Research and Markets, the global zirconia market is expected to reach approximately USD 3.86 billion by 2026, demonstrating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 8% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is driven by the unique characteristics of zirconia, such as its exceptional strength, low density, and high-temperature resistance, which are essential in environments where traditional materials may falter.
In aerospace applications, zirconia ceramic is increasingly utilized in turbine engines and heat exchangers due to its ability to withstand extreme temperatures while maintaining structural integrity. Similarly, in the automotive industry, the incorporation of zirconia components in fuel cells and exhaust systems enhances thermal efficiency and reduces emissions. A study published in the Journal of Materials Science highlighted that zirconia's thermal conductivity is significantly lower than that of metals, which aids in thermal management and contributes to overall vehicle performance. As industries strive for sustainability and improved performance, the role of zirconia ceramic continues to expand, positioning it as a leading material for future innovations.
Zirconia ceramic has emerged as a formidable alternative to traditional materials in various modern applications due to its superior properties. According to a recent report by the Institute of Advanced Materials, zirconia exhibits a fracture toughness of approximately 8 MPa·m^1/2, significantly higher than typical alumina ceramics, which range from 3 to 4 MPa·m^1/2. This enhanced toughness makes zirconia ideal for dental applications, where durability and longevity are paramount. In addition to its mechanical advantages, zirconia also demonstrates excellent resistance to wear and corrosion, outperforming metals and traditional ceramics in environments subject to harsh conditions.
Moreover, a comparative analysis reveals that zirconia ceramics maintain their structural integrity in high-temperature situations better than many conventional materials. A study published in the Journal of Materials Science indicated that zirconia can withstand temperatures exceeding 1,500°C, while traditional materials such as porcelain or glass-ceramics tend to degrade or deform beyond 1,200°C. This temperature resilience not only extends the lifespan of zirconia applications in industries like aerospace and automotive but also enhances safety and performance standards. As industries continue to seek innovative solutions, the unique properties of zirconia ceramics position them as a compelling choice over traditional materials.
Zirconia ceramic has emerged as a key player in modern manufacturing, particularly due to its sustainability and adaptability. This innovative material is gaining traction in various industries, from dental applications to aerospace engineering. One of the primary benefits of zirconia is its durability, which minimizes waste by reducing the need for frequent replacements. Additionally, its production process can be optimized to reduce energy consumption and lower carbon emissions, aligning with the growing push for sustainable practices in manufacturing.
As trends evolve, manufacturers are increasingly focused on sourcing sustainable materials. Zirconia ceramic fits this bill perfectly, as it can be produced using eco-friendly methods and is fully recyclable. Furthermore, the development of advanced zirconia composites is paving the way for lighter, stronger materials that maintain high performance while also being environmentally responsible. This shift not only enhances product lifespan but also demonstrates a commitment to sustainability—a crucial factor for industries looking to meet regulatory standards and consumer expectations in an eco-conscious market.