Leave Your Message
In the industrial world, materials play a vital role. One such material is Technical Ceramic. This high-performance substance is known for its durability and resistance to extreme conditions. It has become essential in various industries, from aerospace to electronics.
Using Technical Ceramic requires understanding its properties. These ceramics can withstand high temperatures and corrosive environments. They also offer excellent electrical insulation. However, not all applications suit Technical Ceramic perfectly. Misuse can lead to failures and inefficiencies. Therefore, reflecting on material choice is crucial.
Choosing Technical Ceramic is often a double-edged sword. While it offers many benefits, it can also present challenges. Engaging with this material means balancing its strengths and weaknesses. Industrial applications demand precision, and Technical Ceramic can provide that—when used correctly.

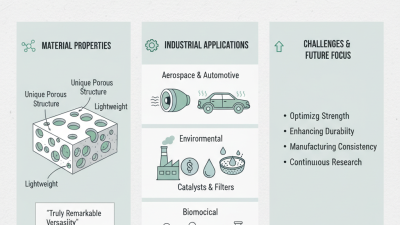
Technical ceramics play a vital role in various industrial applications. These materials are known for their excellent hardness and wear resistance. Commonly used ceramics include alumina, zirconia, and silicon carbide. Their ability to withstand extreme temperatures and corrosive environments makes them ideal for manufacturing processes. For example, in the aerospace industry, they can be found in turbine engines and thermal barriers.
In the electronics field, technical ceramics serve as insulators and capacitors. They offer high dielectric strength and thermal stability. However, the production process can be challenging. Controlling the microstructure is crucial for ensuring optimal performance. Small variations can lead to significant differences in properties. This is an area where continuous improvement is necessary.
The automotive industry also benefits from technical ceramics. They are used in braking systems and engine components. The lightweight nature of ceramics helps improve fuel efficiency. Yet, cost remains a concern. The high prices can hinder broader adoption. Finding balance is essential. Understanding these materials deeply is imperative for future developments in industrial applications.
| Application Area | Ceramic Type | Properties | Advantages | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Silicon Nitride | High strength, low weight, thermal stability | Reduced weight, increased efficiency | Engine components, turbine blades |
| Medical Devices | Alumina | Biocompatibility, wear resistance | Safe for human contact, long-lasting | Dental implants, surgical instruments |
| Electronics | Zirconia | High dielectric strength, thermal insulation | Improved durability, heat resistance | Substrates for electronic components |
| Automotive | Hafnium Carbide | High melting point, chemical stability | Resistant to extreme conditions | Engine parts, valve components |
| Industrial Machinery | Boron Nitride | Lubricative properties, thermal conductivity | Reduced friction, improved efficiency | Cutting tools, bearings |
Technical ceramics have unique properties that make them ideal for various industrial applications. Their exceptional hardness is one of the most notable features. For instance, they can withstand high wear without significant degradation. According to a report by the International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, some ceramics have a hardness rating of over 9 on the Mohs scale. This incredible resilience significantly reduces maintenance costs in manufacturing.
Another crucial property is thermal stability. Technical ceramics can perform in extreme temperatures, often exceeding 1,000 degrees Celsius. This capability is pivotal in industries such as aerospace and automotive, where materials face harsh conditions. Many manufacturers report improved efficiency with ceramics that have excellent thermal insulation properties. Yet, this does not come without challenges. The brittleness of ceramics can lead to unexpected failures if not adequately accounted for in design.
Additionally, ceramics exhibit impressive chemical resistance, making them suitable for corrosive environments. However, the fragility of some ceramic materials may necessitate careful handling during installation. Surveys indicate that nearly 30% of companies face issues related to brittle fracture in ceramic components. This highlights the need for thorough testing and adaptation of these materials in real-world applications.
Technical ceramics play a crucial role in various industrial applications. These materials are known for their strength, durability, and resistance to high temperatures. One key area is the aerospace industry. Here, technical ceramics are used in engine components and thermal protection systems. They withstand extreme conditions. This makes them vital for flight safety and efficiency.
Another significant application is in the medical field. Technical ceramics are commonly used in implants and prosthetics. They are biocompatible, meaning they interact well with human tissue. Their wear resistance is impressive, though the challenge lies in ensuring a perfect fit. Small fabrication errors can lead to failure. Continuous improvement in manufacturing techniques is essential.
Electrical insulators are another area where ceramics excel. They provide high dielectric strength and thermal stability. This is crucial for components in power transmission and communication systems. However, the interface between ceramics and other materials can be problematic. Proper bonding techniques must be developed to enhance performance and reliability. These challenges highlight the ongoing need for innovation in the field.
When selecting the right type of technical ceramic for industrial applications, consider several factors. Different ceramics have distinct properties. For example, alumina is renowned for its excellent wear resistance. Zirconia, on the other hand, offers superior toughness. Think about what your project needs. What environment will the material face? High temperatures? Chemical exposure? Each ceramic's unique characteristics suit various applications.
Evaluate the application requirements closely. Precision components may require tight tolerances. A high-friction environment may demand superior hardness. Sometimes, it is easy to overlook the size and shape constraints of the ceramic parts. Reflect on whether the selected material can be manufactured in the desired form without excessive costs. Always keep in mind that failure to select the right material can lead to defects.
Testing is vital. Prototype parts and conduct performance tests to benchmark their effectiveness. Don't be surprised if initial selections don't work as planned. It is common to iterate on materials. Learning from failures can lead to better decisions down the line. The process is crucial in industrial applications where reliability is paramount.

Technical ceramics are increasingly popular in industrial applications. These materials offer several advantages, but they also come with challenges. They are known for their exceptional hardness and wear resistance. This makes them perfect for parts that need to withstand harsh conditions. For instance, they are widely used in cutting tools and wear-resistant components.
However, using technical ceramics isn't without difficulties. They can be brittle, which makes handling and machining complicated. Manufacturing processes often require precise conditions to prevent defects. Cost can be another issue, as high-quality ceramics may be more expensive than traditional materials. Moreover, surface finishing might be needed, adding to the overall production time.
Despite these challenges, the benefits can outweigh the drawbacks. Success in utilizing technical ceramics depends on understanding their properties. Engineers must consider the application requirements carefully. Finding the right balance between performance and cost is crucial. Each industrial application may require a unique approach to harness the potential of these materials effectively.