Refractory Kiln Furniture in Industrial Furnaces: An Overview
1. Key Types of Refractory Kiln Furniture
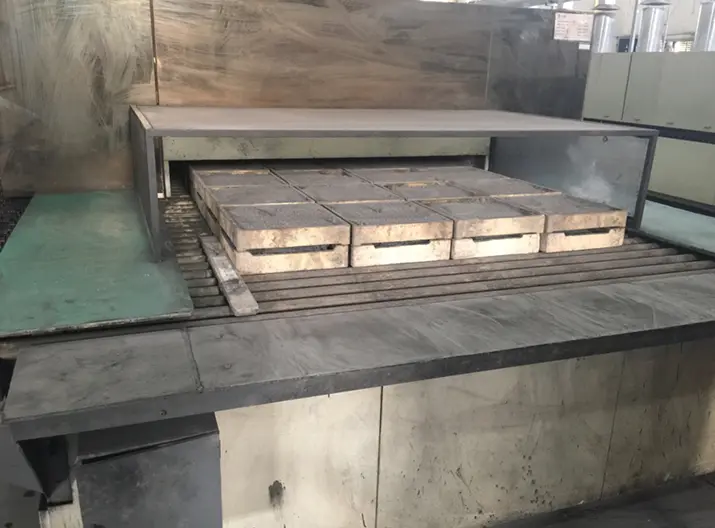
1.1 Kiln Cars (Trolleys)
Kiln cars are mobile platforms that transport batches of products through tunnel or shuttle kilns. Constructed from high-alumina or silicon carbide composites, they feature layered insulation to minimize heat loss. Their design prioritizes load-bearing capacity and thermal shock resistance, ensuring longevity despite repeated exposure to temperature gradients. Modern kiln cars often incorporate lightweight refractory ceramics to reduce energy consumption during cycling.
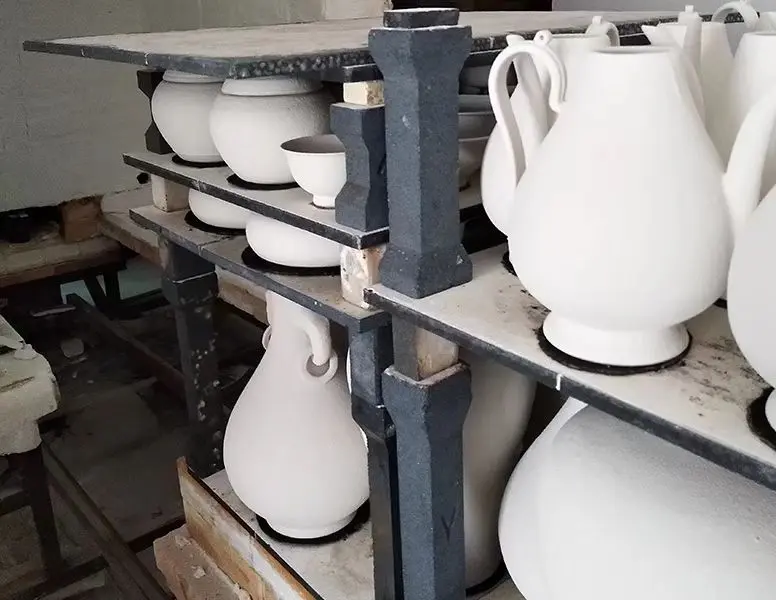
1.2 Shelves (Setter Plates)
Setter plates, or Kiln Shelves, provide flat surfaces to hold ceramic or metal products during firing. Made from recrystallized silicon carbide (R-SiC) or alumina-mullite, these plates resist deformation under load at high temperatures. Their low thermal expansion coefficients prevent cracking during heating/cooling cycles, while their smooth surfaces minimize contamination. Advanced designs include perforated shelves to improve heat distribution in precision applications like electronic ceramics.
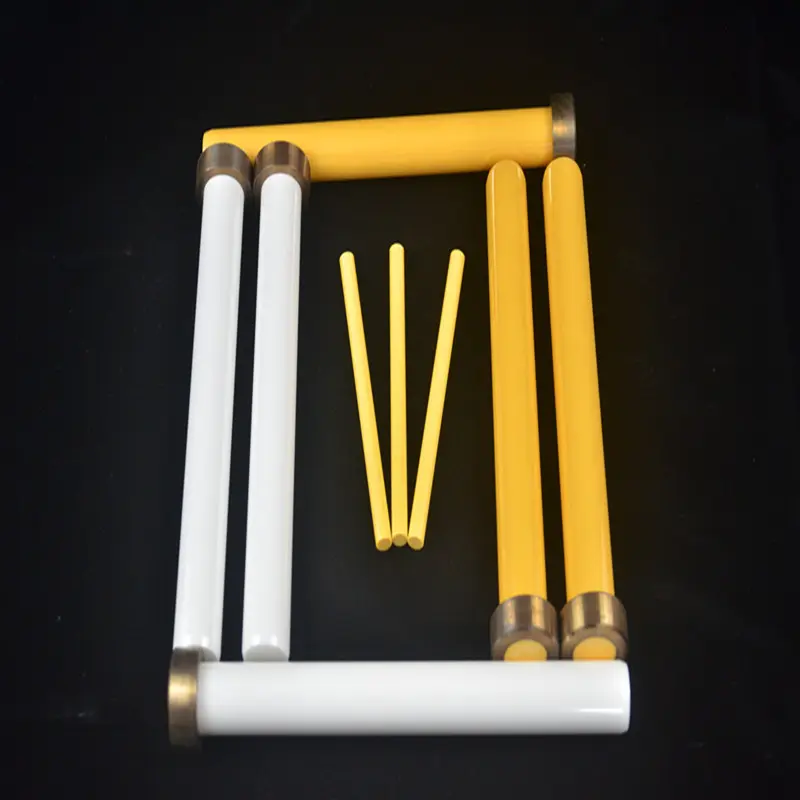
1.3 Posts and Pillars
Vertical supports, such as posts and pillars, elevate shelves to create multi-tiered stacking systems. Mullite-based pillars are favored for their creep resistance, maintaining dimensional stability during prolonged firing. In reducing atmospheres, silicon nitride-bonded silicon carbide (Si3N4-SiC) offers superior strength and oxidation resistance. These components are engineered to distribute weight evenly, preventing sagging in kilns operating above 1400°C.
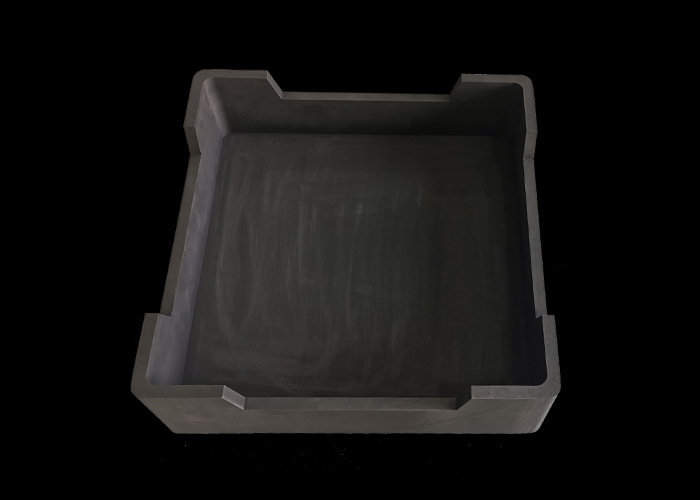
1.4 Saggers (Protective Containers)
Saggers—box-like containers—shield sensitive materials (e.g., catalysts, nuclear fuels) from direct flame contact and gaseous byproducts. Traditional saggers use cordierite for its low thermal expansion, while high-purity alumina linings are employed in corrosive environments. In semiconductor manufacturing, ultra-dense zirconia saggers prevent contamination during wafer annealing.
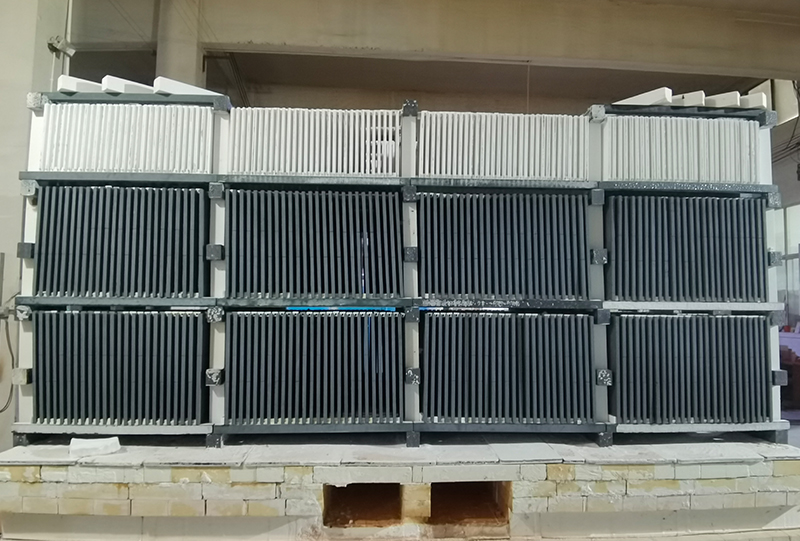
1.5 Ceramic Rollers
Used in roller hearth kilns, these cylindrical rods enable continuous processing of glass or tiles. Alumina-zirconia composites dominate this category due to their wear resistance and ability to endure bending stresses at temperatures up to 1300°C. Precision-ground surfaces ensure smooth rotation, critical for maintaining product alignment in high-speed operations.
1.6 Thermocouple Protection Tubes
These tubes house temperature sensors in hostile furnace environments. Dense alumina or magnesia-stabilized Zirconia Tubes provide electrical insulation and resist slag penetration. In hydrogen-rich atmospheres, yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) is preferred for its ionic conductivity stability.
2. Material Selection Criteria
Refractory kiln furniture materials are chosen based on:
-
Thermal Stability: Resistance to deformation (creep) at peak temperatures.
-
Thermal Shock Resistance: Ability to survive rapid temperature changes without cracking.
-
Mechanical Strength: Compressive and flexural strength under load.
-
Chemical Inertness: Compatibility with furnace atmospheres (oxidizing, reducing, or vacuum) and processed materials.
-
Cost Efficiency: Balancing performance with lifecycle costs.
Common Materials:
-
Silicon Carbide (SiC): Superior thermal conductivity (15–20 W/m·K) and strength up to 1600°C, ideal for fast-firing cycles. Vulnerable to oxidation above 1200°C unless coated.
-
Alumina (Al2O3): High hardness and chemical purity (>99%), suitable for electronics and aerospace components. Prone to brittle fracture under thermal stress.
-
Mullite (3Al2O3·2SiO2): Excellent creep resistance and low thermal expansion, optimal for long-duration firings.
-
Cordierite (2MgO·2Al2O3·5SiO2): Low thermal expansion (1–2 ×10⁻⁶/°C), used in saggers and insulating components. Limited to temperatures below 1200°C.
3. Innovations and Trends
Recent advancements focus on enhancing durability and sustainability:
-
Composite Materials: SiC-AlN composites improve oxidation resistance, while fiber-reinforced alumina boosts fracture toughness.
-
Additive Manufacturing: 3D-printed lattice structures reduce weight and thermal mass, cutting energy use by 15–20% in batch kilns.
-
Recyclability: Manufacturers now design modular kiln furniture with replaceable wear parts, extending service life and reducing waste.
4. Application-Specific Considerations
-
Ceramics Production: SiC shelves dominate due to rapid heat transfer in fast-fire kilns.
-
Steel Annealing: Mullite-based cars withstand prolonged exposure to 1350°C in hydrogen atmospheres.
-
Glass Tempering: Zirconia rollers prevent adhesion to molten glass surfaces.
5. Conclusion
Refractory kiln furniture is the unsung enabler of industrial high-temperature processes. As material science progresses, next-generation composites and smart designs promise greater efficiency, lower emissions, and adaptability to emerging technologies like lithium-ion battery sintering and additive manufacturing. Selecting the appropriate kiln furniture requires a nuanced understanding of operational parameters, underscoring its pivotal role in industrial thermal engineering.