The Role of Graphite Sagger in Sintering Negative Electrode Materials
Sintering is a thermal process that involves the consolidation of powder materials into a solid mass through heat and pressure. In the case of negative electrode materials, which are often composed of various carbon-based compounds, the sintering process must be carefully controlled to achieve the desired electrical and mechanical properties. Graphite sagger serves as a protective container during this process, providing several advantages.
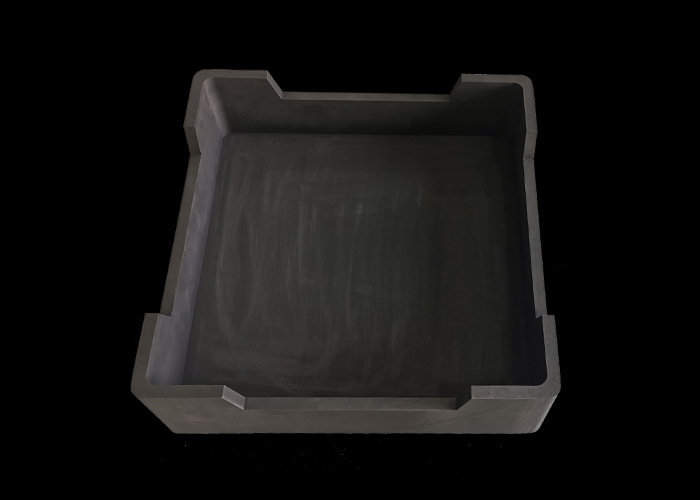
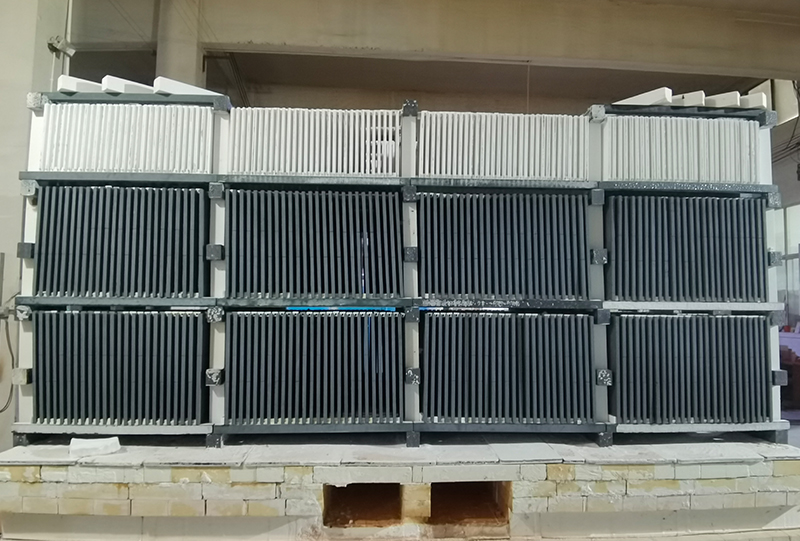
Firstly, graphite saggers are known for their excellent thermal conductivity, which ensures uniform heat distribution during sintering. This uniformity is essential for achieving consistent material properties across the entire batch of negative electrode materials. Additionally, graphite’s high resistance to thermal shock allows it to withstand the extreme temperatures often required in the sintering process without deforming or breaking.
Moreover, the use of graphite sagger minimizes contamination risks. Traditional sintering containers may introduce impurities that can adversely affect the performance of the negative electrode materials. In contrast, graphite is chemically inert at high temperatures, ensuring that the integrity of the materials is maintained throughout the sintering process.
In conclusion, the application of graphite sagger in the sintering of negative electrode materials is a vital aspect of modern battery manufacturing. By providing excellent thermal management, reducing contamination risks, and enhancing the overall quality of the final product, graphite saggers are indispensable tools in the quest for more efficient and reliable energy storage solutions. As technology advances, the role of graphite saggers will likely become even more significant in the development of next-generation batteries.